Explore the advantages of company formation in the UAE, especially in Dubai. Our guide simplifies the process, highlighting Dubai’s business opportunities, tax benefits, and diverse company options in the United Arab Emirates.
Opening a Company in Dubai: Advantages of the UAE
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location and Capital | The United Arab Emirates (the UAE), an independent federated state on the southern coast of the Persian Gulf. Capital: Abu Dhabi. |
| Emirates | Comprises seven Emirates: Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Sharjah, and Umm Al Quwain. |
| Currency | National currency is the UAE dirham (AED), pegged to the US dollar. 1 AED is equal to about 0.27 US dollars. |
| Language | Official language is Arabian. English is widely used in the business environment. Governmental websites also have an English version. |
| Business Infrastructure | Advanced commercial and financial infrastructure, particularly in Dubai. Suitable for company formation. |
| Tax Regime | Favourable tax regime for various types of companies. |
| Options for Foreign Investors | Offers diversified options for foreign investors, including obtaining a long-term resident visa. |
| Free Trade Zones (FTZ) | Numerous FTZs, including those focused on specific industries. Some Emirates still offer offshore companies. |
| Ownership Rules | Allows 100% foreign ownership for both FTZ and mainland companies. Available for residents of any country. |
| Foreign Exchange Control | No foreign exchange control and no rules for controlled foreign companies. |
| Economic Freedom Ranking | Holds the 33rd place of 177 in the 2022 economic freedom ranking, leading in the region. Classified as a “mostly free” country by the Heritage Foundation. |
Types of companies in the UAE. Company formation in Dubai
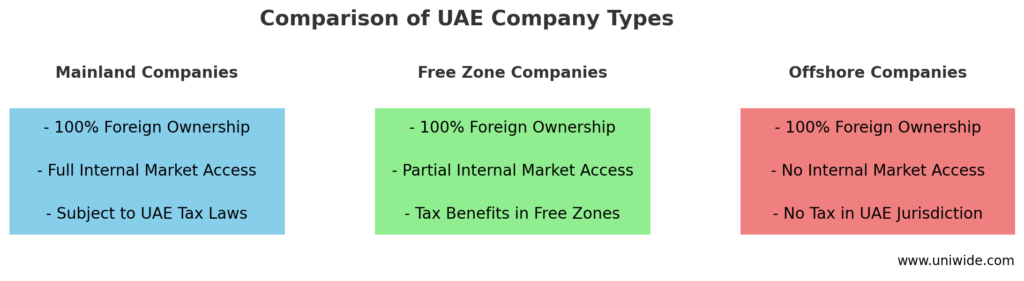
The UAE companies can be divided into three groups depending on the territorial scope of their operations:
- Local (mainland) companies;
- Companies registered in free trade zones (FTZ);
- Offshore companies.
While local and FTZ companies can operate within the UAE (albeit under different conditions), offshore companies can only operate outside the UAE.
For example, one can open a company in Dubai either in its main territory or in any of Dubai’s free trade zones, which provide unique conditions for international business.
Formation of Local (mainland) companies
- Company Registration: Local (mainland, onshore) companies are registered in the UAE mainland (not in free zones) and are designed for full-scale operations in the UAE. They may carry out their activities both within and outside the UAE.
- Taxation and Reporting: Before the federal corporate tax implementation (starting from 1 June 2023 at a 9% rate), local UAE companies are not subject to taxation, including corporate income tax, capital gains, and withholding tax. Exceptions apply to the oil and gas sector and foreign banks.
- Foreign Ownership: From 1 June 2021, local companies in the UAE can be wholly owned by foreigners. Previously, a local partner (“sponsor”) with at least 51% ownership was required. Now, these restrictions remain only for companies operating in the industries specified by the government and those owned by the federal or Emirate-level governments.
- Directors: No citizenship or residency restrictions for company directors, except in strategic industries where the UAE nationals’ participation is regulated.
- Office and Capital: Local companies must have a physical office in the UAE and fully paid-up share capital.
- Financial Statements: All local companies must prepare and submit audited financial statements.
- Tax Residence Certificates: Local companies can obtain tax residence certificates in the UAE to apply double taxation treaties.
Free Zone Companies
There are several dozen free trade zones (FTZ) in the Emirates. Some are universal, and some specialise in specific industries, such as manufacturing, IT, finance, science and technology). FTZ companies in the UAE are one of the most attractive instruments for foreign investors wishing to register their business in Dubai or other Emirates.
- Operations and Activities: Company setup in the UAE can include forming FTZ companies that operate within free zones based on their license and outside the UAE. Companies may not carry out their business directly within the UAE mainland. Such activities are possible only through a local agent or distributor.
- Taxation: Companies residing in a free zone enjoy full tax exemption. After the implementation of the corporate tax (which is to be introduced for the tax periods starting from 1 June 2023 with a 9% rate), such companies will remain exempt, provided that they do not operate in the main territory of the UAE or with local companies in the UAE. Free zone companies which satisfy tax residency criteria can obtain tax residence certificates and apply the double tax treaties to which the UAE is a party.
- Reporting and Audit: A company must prepare and file annual financial statements. Some free trade zones also require financial statements to be audited.
- Ownership and Capital: 100% foreign ownership of a free zone company is permitted. There are no restrictions on the repatriation of profits or capital by foreign investors. Share capital must be paid up. Minimum capital requirements may vary depending on a specific FTZ.
- Directors: There are no citizenship or residency requirements for directors or shareholders.
- Office: A real (physical) office within the Emirates is not required.
FTZ authorities may set different rules and requirements for companies registered within the free zones (for example, minimum capital, reporting and audit, company types by structure and purposes).
We Register Companies in Leading Free Zones
Choosing a Free Zone
The optimal choice of Emirati FTZ for business registration depends on several factors – purposes of company incorporation, nature of its business, specific infrastructure needs, administration costs and others. A business setup consultant can help you identify the most suitable free zone. We work with most Free Zones in Dubai and other Emirates, including:
- Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC),
- International Free Zone Authority (IFZA),
- Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA),
- Meydan,
- Dubai Airport Free Zone (DAFZ),
- Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC),
- Dubai Internet City,
- Dubai Silicon Oasis (DSO),
- Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM),
- Ajman Free Zone (AFZ)
- Sharjah Airport International Free Zone,
- Sharjah Media City (Shams),
- Ras Al Khaimah Economic Zone (RAKEZ),
- Fujairah Free Zone (FFZ),
- Sharjah Research, Technology, and Innovation Park (SRTIP)
- and others.
UAE offshore companies
The third type of company is a “classic” offshore company that enjoys total exemption from taxes in the UAE and operates exclusively outside the country of its incorporation (the UAE).
Offshore companies in the UAE may act as holding companies and own assets, but they may not obtain a business license in the Emirates, do business with the UAE residents or employ them.
Foreign shareholders may fully own an offshore company in the UAE. No residency or citizenship requirements exist for directors and (or) shareholders. A real (physical) office within the UAE is also not required. A company has no duty to submit its financial statements or conduct an audit (except Jebel Ali Free Zone).
Since offshore companies do not meet all tax residency criteria, they cannot obtain a tax residence certificate and use double tax treaties.
Currently (2022), the offshore companies’ regime remains only in three Emirates (along with local and FTZ companies):
- Ras Al Khaimah – RAK International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC);
- Dubai – Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA); and
- Ajman – Ajman Free Zone.
Taxation in the UAE
- Corporate Tax: Starting from June 1, 2023, the UAE has introduced a corporate tax on profits. This applies to both mainland UAE companies and free zone companies. The tax base consists of the company’s worldwide income (earned both in the UAE and abroad), minus expenses.
- Corporate Tax Rate: The corporate tax rate in the UAE is 0% for profits up to 375,000 dirhams (about 102,000 US dollars). A standard rate of 9% applies to profits exceeding this threshold. There’s also a temporary tax exemption for small businesses (for tax periods up to and including 2026). Companies with revenue below 3 million dirhams in the current and previous tax periods can benefit from this.
- Corporate Tax for Free Zone Companies: Free zone companies in the UAE can either follow the standard taxation regime or opt for a 0% rate. The latter is possible if the company is a “qualified” free zone resident. To qualify, a company must predominantly earn “qualified” income, maintain a sufficient presence in the Emirates, and submit audited financial statements.
- VAT: Since January 1, 2018, the UAE has implemented a value-added tax (VAT) at a rate of 5%. It applies to the supply of goods and services and imports. VAT registration is required if a company’s taxable transactions over the past 12 months exceeded 375,000 dirhams.
The UAE residence visa
The UAE residence visa is a residence permit in the Emirates for a more or less long period – from 1 to 10 years. A residence visa may be issued to a foreign person who is already in the UAE on the basis of an entry permit or a short-term or long-term tourist visa.
The UAE residence visa entitles you to:
- open bank accounts in the UAE;
- use various financial products;
- obtain a driving license;
- use state healthcare services and medical insurance;
- enrol your children in state and private schools;
- travel without visas to a number of countries.
There are several ways to obtain a UAE residence visa. A foreign person may apply for a residence visa if he or she:
- Is employed in a UAE company (“working visa”); or
- Is an owner (founder/shareholder having at least 25% interest) of a company registered in the UAE mainland or one of the Emirates’ free trade zones (“investor visa”); or
- Purchases residential property in the UAE (“real estate owner’s visa”).
An applicant’s children, parents and close relatives may also obtain a residence visa.
Opening a bank account in the UAE
- Types of Banks in the UAE: Emirati banks and banks belonging to international financial groups (Europe, USA), catering to businesses after registering a company, operate in the UAE.
- Account Opening Procedures: When opening personal and corporate bank accounts, banks in the UAE, like anywhere else, carry out due diligence and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures, requesting various documents and assessing the risks of accepting each client. Furthermore, banks carry out the subsequent control of account transactions. The legislation on combating money laundering and terrorist financing is in force.
- Focus on UAE Residents: Emirates’ banks primarily focus on servicing UAE residents (local and FTZ companies and individuals with a residence visa and Emirates ID).
- Requirements for Opening Accounts: When opening and maintaining local companies’ accounts in the UAE, banks check, among other things, the presence of a real office and addresses and contact numbers of all shareholders and account holders in the UAE.
- Initial Investments: Opening accounts in the UAE for non-residents is usually subject to the significant investment made by the latter (for example, depositing a certain amount) and meeting all other bank’s requirements.
For comfortable use of the UAE bank account, the account holder needs to speak English at a level that allows effective communication with the bank manager on emerging issues.
We Help Open Accounts with Leading Banks
The Cost of Registering a Company in the UAE
The cost of registering a company in the UAE, particularly in Dubai, varies significantly depending on several factors. These include the type of your business, the choice between a free economic zone or the mainland for your location, and the number of visas and shareholders in your company.
| Service Name | Price |
|---|---|
| Mainland company formation in Dubai, excluding employee visa costs | from AED 16,100 (approx. $4,400) |
| Processing of first visa for a founder or employee, including Establishment Card fee | AED 4,330 |
| Each subsequent visa | AED 3,730 |
| Company formation in a Free Zone (cost varies by Free Zone) | from AED 5,500 (approx. $1,500) |
FAQs About UAE Company Formation
What are the registration timeframes in the UAE?
Registration timeframes depend on the chosen zone. In Free Zones, it usually takes five to seven working days. Mainland company registration can take two to three working days if you have all required documents.
Is a registered office address required to register a company in the UAE?
In a Free Zone, a registered office address is often assigned automatically, unless you need a real office. A Mainland company must have a physical office, and we can help you find one.
What are the requirements for a company’s legal address in the UAE?
There are no strict rules for a legal address, but it must be a commercial premises (for example, a rented shop). Many Free Zones offer virtual office options, and you can update your address later by notifying the registration authority.
Is it possible to register a company in the UAE remotely without the founder’s visit?
Yes, if you register in a Free Zone. In Mainland, the founder must be present. They also usually make one trip for a resident visa and bank account opening.
Does the company founder need a work permit in the UAE?
This is not needed at the registration stage. However, banks typically require at least one founder to have a UAE resident visa when opening a bank account.
Which is faster: registering with individual shareholders or corporate shareholders?
Registration is quicker with individual shareholders. Corporate shareholders involve more checks and documents, which extend the process.
Is it possible to open a sole proprietorship in Dubai or other Emirates?
In the UAE, a sole proprietorship usually falls under a freelance licence. This licence covers specific approved activities, such as design or photography.
Is a freelancer in the UAE an individual or a legal entity?
Under local rules, a freelance licence is closer to a corporate format. The holder remains an independent professional.
What is the minimum share capital for a company in the UAE?
It varies by zone. Mainland companies have no minimum requirement. Some Free Zones, like IFZA, do not require share capital, while others, like DMCC, need at least 50,000 dirhams deposited.
On what terms can the founder or director obtain a UAE resident visa?
A founder qualifies by owning shares. A director qualifies as an employee. Such visas typically last two to three years and can be renewed.
Do you provide accounting and tax support for UAE companies?
Yes. Our team handles bookkeeping, prepares reports, and manages tax filings. We also liaise with local authorities.
Are UAE nationals required as employees when forming a company?
Usually no. Foreign founders can operate without local hires. Mainland companies with over 50 staff might need to employ a certain number of UAE nationals.
What is the maximum period a company can be dormant in the UAE?
You must renew companies every year. Some Free Zones allow freezing company operations for up to five years if you pay the required fees.
Is wholesale trading possible in the UAE without importing goods into the country?
Yes. Many companies do this by making deals with foreign suppliers without moving goods through the UAE.
UAE Company Formation with Uniwide Advisors
Welcome to the world of professional business registration with Uniwide Advisors.
- Registration Timeline: We can assist you in registering a local company in the UAE, particularly in Dubai, or a company in any free zone within as little as two days.
- Licenses and Documents: We will obtain all necessary licenses and permits.
- Resident Visas: We will process resident visas for the founders and employees of the company.
- Expert Consultations: We offer consultations on business relocation to the UAE, taxation, and corporate accounting.
- Bank Accounts: Assistance in opening bank accounts.
Why Choose Us
- Over 15 Years of Experience: We have unique experience and knowledge in company formation vital for successfully setting up your business in the UAE (Dubai).
- Extensive Expertise: We have all forms and regulations for registering both local companies in the UAE and companies in free zones. We work closely with the Department of Economic Development (DED) and the administrations of most free economic zones.
- Individual Approach: We will analyze your business concept and help choose the best place for business registration. We will determine the legal form of the company, considering all aspects of the business environment.
- Office Selection Assistance: We will recommend a suitable company address and select office space in Dubai or other UAE regions, considering all criteria.
- Administrative Support: We will represent your interests in UAE government departments and process resident visas for partners, company employees, and their families; we also handle the renewal of all types of licenses and permits.
- Accounting and Tax Support: Assistance with VAT registration and comprehensive accounting and tax services for your company.
